The Brinell hardness test method is to determine Brinell hardness, is in ASTM E10. Generally it is used to test materials that it is too coarse or rough to be tested by using another test method, e.g., castings and forgings. Brinell testing often use a very high test load (3000 kgf) and a 10mm diameter indenter so that the resulting indentation averages out most surface and sub-surface inconsistencies.
The Brinell method applies a preset test load (F) to a carbide ball of fixed diameter (D) which is held for a preset time period and then removed. The resulting impression is measured with a specially designed Brinell microscope or optical system at least two diameters – usually at right angles to each other and these results are averaged. Although the calculation below can be used to generate the Brinell number, most often a chart is then refereed to convert the averaged diameter measurement to a Brinell hardness number.
Common test forces range from 500kgf for non-ferrous materials and to 3000kgf usually used for steels and cast iron. There are also other Brinell scales with load as low as 1kgf and 1mm diameter indenters but these are hardly used.
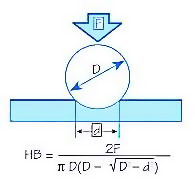
Test Method Illustration
D = Ball diameter
d = impression diameter
F = load
HB = Brinell value
Brinell Hardness tester recommended models: KHT600-A; KHT600-M

 français
français Español
Español русский
русский العربية
العربية português
português
